I thought the "being wrong" versus "lying" was in reference to Fauci and the Wuhan Labs funding. Fauci said adamantly that the CDC or NIH did NOT fund those labs at the time in question. Turns out that maybe they did. I'm betting he had been given bad info on that so was "wrong" instead of actually "lying".
Results 15,601 to 15,625 of 23264
-
10-22-2021, 12:30 PM #15601Go that way really REALLY fast. If something gets in your way, TURN!
-
10-22-2021, 12:41 PM #15602
Sir this is a Wendy’s... errr vaccine thread and Aspen knows better than to talk about rat flu origins here when that discussion is reserved for the other thread, right?
FWIW, the issue isn't whether the NIH provided grant money that went on to fund research at Wuhan Institute of Virology but instead whether the money was used for Gain-Of-Function research. The NIH has denied funding GOF. The latest FOI documents show research was done on mutant SARS-related coronaviruses in mice. The question is whether this work on mice constitutes GOF research and whether the NIH knew about it.
-
10-22-2021, 12:42 PM #15603
Alternative Facts. They exist.
A few people feel the rain. Most people just get wet.
-
10-22-2021, 12:47 PM #15604
 Registered User
Registered User
- Join Date
- Sep 2009
- Posts
- 2,155
You sir are correct. Thanks for taking the time to maintain reading comprehension while others opine on news stories without admittedly reading any of the source material. Same trope as the "I did my own research!" type of people.
The real disservice here is the fact that the head of the NIH has to tweet his formal letter to Congressmen James Comer as no major news outlet wants to report on what could (and should) be considered a significant news story.
Echo chambers do us all a disservice. Branch out with your media consumption.
-
10-22-2021, 01:04 PM #15605
Nonsense. The NYTimes, Newsweek, CNN, Fox News, and many more are all covering the story not only today but have been doing so all along.
-
10-22-2021, 01:14 PM #15606
 Registered User
Registered User
- Join Date
- Sep 2009
- Posts
- 2,155
The letter from HHS to the congressmen was dated 10/20/21, so this would be recent news. Please provide links showing these news articles reference Lawrence Tabak's letter.
In your earlier post you split hairs by saying the testing for gain of function research was happening to mice. You do know what humanized mice are, and their purposes, correct?
-
10-22-2021, 01:18 PM #15607
I said, "research was done on mutant SARS-related coronaviruses in mice. The question is whether this work on mice constitutes GOF research and whether the NIH knew about it." The subject was mutant SARS-related coronaviruses, mice were incidental although many will argue that's an important distinction. So depending on your expert opinion and/or political bent the questions are:
1 - Did EcoHealth Alliance violate the terms and conditions of NIH grant
2 - Was the research GOF or something else
3 - Is making a virus that's modestly worse in mice the same as creating a more transmissible pathogen in humans
In your earlier post you disingenuously accused someone of making a false claim, why?
-
10-22-2021, 01:18 PM #15608
So news outlets are the official form of government inter office communications now?
A few people feel the rain. Most people just get wet.
-
10-22-2021, 01:19 PM #15609
https://www.nytimes.com/2021/10/21/s...-leak-nih.html
Sent from my iPhone using TGR Forums
-
10-22-2021, 01:20 PM #15610
Dick Enbright is not the head of NIH. Nor is Lawrence Tabak. It's Francis Collins still until his retirement is official.
Now consume this, since the actual question was not "Did NIH fund the WIV?", but specifically "Did the NIH fund gain of function research in pathogens with pandemic potential at the WIV?"
What I consider to be "source" material isn't a web based news compiler- it's the actual Ecohealth summary submitted to NIH.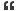 Originally Posted by https://www.science.org/content/article/nih-says-grantee-failed-report-experiment-wuhan-created-bat-virus-made-mice-sicker
Originally Posted by https://www.science.org/content/article/nih-says-grantee-failed-report-experiment-wuhan-created-bat-virus-made-mice-sicker
Full results summary3.1 In vivo infection of Human ACE2 (hACE2) expressing mice with SARSr-CoV S protein
variants
In Year 5, we continued with in vivo infection experiments of diverse bat SARSr-CoVs on
transgenic mice expressing human ACE2. Mice were infected with 4 strains of SARSr-CoVs
with different S protein, including the full-length recombinant virus of SARSr-CoV WIV1 and
three chimeric viruses with the backbone of WIV1 and S proteins of SHC014, WIV16 and
Rs4231, respectively. Pathogenicity of the 4 SARSr-CoVs was evaluated by recording the
survival rate of challenged mice in a 2-week course. All of the 4 SARSr-CoVs caused lethal
infection in hACE2 transgenic mice, but the mortality rate vary among 4 groups of infected mice
(Fig. 13a). 14 days post infection, 5 out of 7 mice infected with WIV1 remained alive (71.4%),
while only 2 of 8 mice infected with rWIV1-SHC014 S survived (25%). The survival rate of mice
infected with rWIV1-WIV16S and rWIV1-4231S were 50%. Viral replication was confirmed by
quantitative PCR in spleen, lung, intestine and brain of infected mice. In brain, rWIV1, rWIV1-
WIV16S and rWIV1-4231S cannot be detected 2 days or 4 days post infection. However,
rWIV1-SHC014 was detected at all time points and showed an increasing viral titer after
infection. The viral load reached more than 10e9 genome copies/g at the dead point (Fig. 13b).
We also conducted histopathological section examination in infected mice. Tissue lesion and
lymphocytes infiltration can be observed in lung, which is more significant in mice infected with
rWIV1-SHC014 S (Fig. 13d) than those infected with rWIV1 (Fig. 13c). These results suggest
that the pathogenicity of SHC014 is higher than other tested bat SARSr-CoVs in transgenic
mice that express hACE2.
This is not gain of function as broadly defined by "one skilled in the art" as the legalese would say. This was an experiment to define the function/tropism of other naturally occuring Cov's using chimeric viruses by grafting other viral Spike proteins on a nonhuman-infectious WIV1 virus, in lieu of isolation and propagation of the other naturally occuring virus isolates. This was to help to define which of those naturally occurring bat CoV's may have the potential to spill over into humans, not to design a bat/human infecting CoV with a gain of function that enabled human infection.I.1 What were the outcomes of the award?
The aims of our grant (R01AI110964) were to: 1) Analyze the risk that there could be a repeat of the SARS outbreak, due to bat coronaviruses still circulating in China; 2) Work out how we can predict which bat viruses would be most likely to emerge, so that we can prevent new outbreaks; 3) Using lab tests, find out if any of the coronaviruses still present in bat populations in China have the potential to infect people. The overall goal of this work is to help design vaccines and therapeutics against future potentially emerging viruses, work out which communities are on the frontline of a new potential outbreak, and reduce the risk of them being infected by analyzing their risk behavior. During this 5-year period of work, we made significant discoveries leading to 18 peer-reviewed scientific papers, including in some of the world’s foremost scientific journals.
Overall, our work shows that bats in China harbor a high number and diversity of coronaviruses, some closely related to SARSCoV(the virus that caused the SARS pandemic in 2003). We sampled over 16,000 individual bats and found evidence of hundreds of different SARS-related coronavirus genetic sequences. We found out that bats across China harbor these viruses, and that they are common, with 6.7% of bats sampled being positive. Many of these bats are found across China, Southeast Asia, South Asia and beyond, suggesting viruses with zoonotic potential may exist in those regions also. Many of these bats are abundant, and roost and feed close to people and livestock, suggesting high potential for future viral spillover. We also identified one cave system in Yunnan Province with horseshoe bats that had diverse SARSr-CoVs, including some with S proteins able to use human ACE2 as entry receptors. Bats in this cave carried SARSr-CoVs with all unique genetic elements of the SARS-CoV outbreak virus, suggesting that this site may be a potential public health risk.
To analyze which viruses were a potential public health risk, we managed to culture three strains of SARSr-CoVs from bat feces: WIV1, WIV16 and Rs4874. We used the genetic codes of some of the other viruses we found in bats and inserted the spike protein genes of those viruses (the proteins that attach to cells) into the cultured viruses. By doing this experiment we showed that other viruses may also be able to infect human cells, and were able to do this safely without the need to culture large amounts of virus. We also showed that some of these viruses cause SARS-like illness in mice that are adapted to have similar cell surface receptors to people. This work proves that there is a clear and present danger for future emergence of novel SARS-like viruses in people.
We also demonstrated that outbreaks can happen in livestock. In 2016-17, we analyzed fecal samples from pigs at 5 farms in South China affected by a fatal diarrheal disease. We discovered a new coronavirus, Swine Acute Diarrheal Syndrome coronavirus (SADS-CoV), and showed that it originates in bats, caused the death of more than 20,000 pigs, but also is able to infect human cells in the lab.
Our work has produced predictive algorithms to map hotspots of viral risk so that public health measures can be taken to protect communities at the frontline of potentially the next SARS pandemic. We have produced new reagents and viral cultures that can be used by labs across the world to design novel vaccines and therapeutics against SARS-CoV and other related viruses that might emerge in the future. Finally, our work has been used directly by the WHO to list SARS-related coronaviruses as one of the highest priority group of pathogens with pandemic potential, so that efforts can be taken to stop a future pandemic before it happens.
However.
IMO it is a bit disingenuous to say the results of increased lethality were "unexpected", since this type of experiment fundamentally addresses a simple question whether the lethality of the chimeric viruses with the other grafted BatCoV species Spike variants is increased, decreased, or the same as that of the non-chimeric WIV1 strain.Move upside and let the man go through...
-
10-22-2021, 01:40 PM #15611
WaPo last MAY
Fact-checking the Paul-Fauci flap over Wuhan lab funding
Newsweek over a month ago..
TECH & SCIENCE
Fauci Was 'Untruthful' to Congress About Wuhan Lab Research, New Documents Appear To Show
USA Today June
'I remember it very well': Dr. Fauci describes a secret 2020 meeting to talk about COVID origins
Yep total lamestream media blackout!Go that way really REALLY fast. If something gets in your way, TURN!
-
10-22-2021, 01:44 PM #15612
Throw in a comment that has anything to do with the flu. Or even mentions the flu.
Then add in some sarcastic comments feigning concern.
Include Fauci and mainstream media and you’ll get the full bonus from your troll farm masters.
-
10-22-2021, 01:47 PM #15613
 Registered User
Registered User
- Join Date
- Sep 2009
- Posts
- 2,155
Did hell just freeze over because the resident expert just agreed with me with his last sentence RE: what kind of research the NIH is funding.
I see Eco Health Alliance getting chucked under the bus for this, with NIH distancing themselves as fast as possible.
The inherent issue though is that the NIH funds this research and (should) be providing oversight to said taxpayer funded research.
-
10-22-2021, 01:57 PM #15614
Experts will agree with you when are right.
So I’d guess they’ll agree with around 0.5% of your posts (and even then have to ignore the included bullshit behavior)
-
10-22-2021, 02:00 PM #15615
Ignore is a wonderful gain of function.
A few people feel the rain. Most people just get wet.
-
10-22-2021, 02:02 PM #15616
 Registered User
Registered User
- Join Date
- Mar 2008
- Location
- northern BC
- Posts
- 34,019
Got a free flu shot yesturday, then had a sativa gummy, feeling rough today
but I think it was the beers on the way home thru the beermuda triangleLee Lau - xxx-er is the laziest Asian canuck I know
-
10-22-2021, 02:02 PM #15617
He's not agreeing with you. Reread his post.
Sorry if I missed it with all the Asspen chum in the water...but are people getting mix and match boosters just by going in? When I try to book an appointment I, for one, don't meet any of the criteria, and two the sites ask me what vaccine I had and then recommends a boost of the same kind. I sort of want to mix in a Moderna shot as a booster if possible. I'm basing this on the Costco and Walgreens sites.Damn shame, throwing away a perfectly good white boy like that
-
10-22-2021, 02:16 PM #15618
Yes, Walgreens website directs you to a store that has what you had, which was 25 miles away from home. After checking them I booked mine this morning at CVS. Had the choice of Moderna of Pfizer. Chose Moderna (kept going back and forth so just went with what I had and the CVS close to my house is Moderna).
They asked no questions online about what I'd had, just dates to make sure I was 6 months out.
Showed up and left after 5 minutes. This store was Moderna but I think they would have given me the shot if my card said Pfizer. He didn't even look at it and sign it till he was ready to shoot me.
It was anticlimactic.
-
10-22-2021, 02:19 PM #15619
-
10-22-2021, 02:30 PM #15620
I just walked myself through it again on CVS and it does ask what you had but it gives you the option to schedule either Pfizer or Moderna even after you tell them.
Sent from my SM-G991U1 using Tapatalk
-
10-22-2021, 02:33 PM #15621
-
10-22-2021, 03:57 PM #15622
Got a txt message from CO state that my vax is over 6mo ago and 'due for booster'. Pretty cool. I'm going to do it. Decisions on the mix-match hmmmm.
-
10-22-2021, 04:02 PM #15623
-
10-22-2021, 04:09 PM #15624
CVS I was picking something up at today only has Pfizer.. That works for wife and kid, both frontline. No Moderna though which is want I'm after to keep pure. Here's the thing though, I'm neither working around other folks nor age 65+. Wife caught the "high risk" fine print that includes "smokers and former smokers".. So I'm in when I find a place shooting Moderna without a wait beyond my patience level.. which is very low hahahaha.. Sam's Club has Moderna right now according to the CDC vaccine search page. I have Nov 1st off. Thinking a weekday would be better than a weekend for walking in and getting it without a wait.
Go that way really REALLY fast. If something gets in your way, TURN!
-
10-22-2021, 04:58 PM #15625I have been in this State for 30 years and I am willing to admit that I am part of the problem.
"Happiest years of my life were earning < $8.00 and hour, collecting unemployment every spring and fall, no car, no debt and no responsibilities. 1984-1990 Park City UT"

 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote





Bookmarks